By Ana Verayo, | December 29, 2016
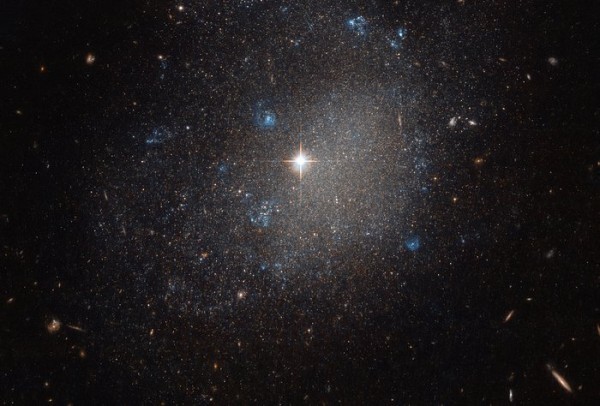

NGC 4707 lies roughly 22 million light-years from Earth. (ESA/Hubble & NASA)
Astronomers have captured a stunning image of a distant spiral galaxy known as NGC 4707, which is located some 22 million light years away from Earth within the Canes Venatici or Hunting Dogs constellation.
This new image was captured by the Hubble Space Telescope using its high-resolution Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), revealing the galaxy in unprecedented detail.
Like Us on Facebook
According to European Space Agency officials, NGC 4707 was first described by British astronomer William Herschel as a small, stellar galaxy and classified as a spiral type with spiraling arms loosely undefined, stretching outwards with a central bulge that is virtually non-existent. Herschel added that this galaxy appears to be a rough sprinkling of stars with flashes of bright blue that are scattered on a dark canvas.
In this new image, the spiral galaxy also has some smoky, blue rings throughout its region. Astronomers believe that these regions are stellar nurseries which stopped producing stars or are still churning out young stars. These blue stars are very hot and massive and were just formed recently while reddish stars are a lot older.
The Hubble Space Telescope was placed into orbit in 1990 by NASA's Discovery space shuttle. It captured a stunning and unprecedented detail of galaxies and nebulae peering back into time when the cosmos was still in its infancy. Millions of other images have been taken by the first ever space telescope. It also saw the first light from 13 billion years ago, providing us the first high-resolution views of our universe.
Hubble also captured NGC 248 which are two nebulae neighbors that are so close to each other and surrounded by a thick cloud of hydrogen gasses. NGC 248 is located some 200,000 light years from Earth. It glows a bright reddish due to powerful radiation that heats up the hydrogen gasses enshrouding the stars within its center.
-
Use of Coronavirus Pandemic Drones Raises Privacy Concerns: Drones Spread Fear, Local Officials Say

-
Coronavirus Hampers The Delivery Of Lockheed Martin F-35 Stealth Fighters For 2020

-
Instagram Speeds Up Plans to Add Account Memorialization Feature Due to COVID-19 Deaths

-
NASA: Perseverance Plans to Bring 'Mars Rock' to Earth in 2031

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
COVID-19: Doctors, Nurses Use Virtual Reality to Learn New Skills in Treating Coronavirus Patients