By Ana Verayo, | January 02, 2017
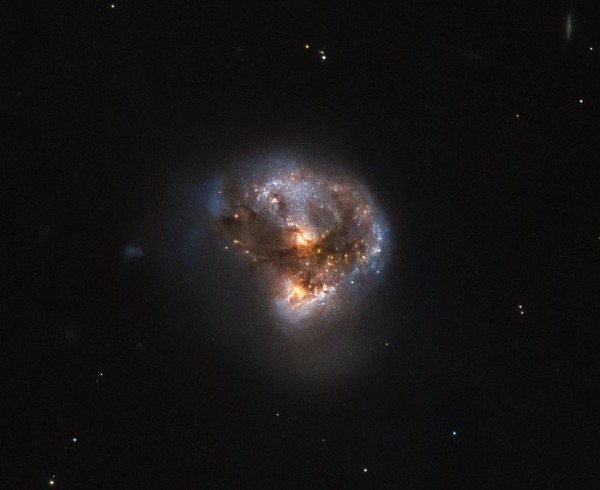

Megamasers are intensely bright, around 100 million times brighter than the masers found in galaxies like the Milky Way. (ESA/Hubble & NASA)
Astronomers have detected a unique, super-bright galaxy some 370 million light years away from Earth, which is home to a "megamaser," a cluster of galaxies that emit powerful microwave radiation.
Like Us on Facebook
Thanks to the Hubble Space Telescope, this galaxy known as the IRAS 16399-0937 is also ultra luminous, about 100 million times more bright than regular masers. Masers are naturally occurring intense and powerful light sources from galaxies and other cosmic objects, more specifically ejecting stimulated spectral line emissions of the microwave kind.
NASA scientists revealed in this new image that this megamaser galaxy is releasing microwave emissions instead of visible light. Within a galaxy, a megamaser can occur inside through its gas clouds and emit powerful energies such as microwave like in the super bright IRAS 16399-0937.
In this image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, the microwave energies emitted by this galaxy were captured in a stunning photograph across this wavelength range, courtesy of the space telescope's Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) and Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS).
Astronomers were able to identify the double nucleus of this galaxy, exposing two cores that seem to be in a merger process. These two nuclei are called IRAS 16399N and IRAS 16399S. They depict the northern and southern regions of the galaxy which span 11,000 light years across.
These two galactic nuclei apparently shows some dynamic activity between each other, within a thick, cosmic swirl of dust and gas that forms a distinct shape.
Astronomers suggest thT the IRAS 16399S nucleus is similar to star-forming regions within a galaxy, as stars are being churned out at a rapid rate.
The northern region IRAS 16399N, on the other hand, is considered as a LINER (Low Ionization Nuclear Emission Region) nucleus where emissions are mostly composed of neutral atoms and weakly ionized atoms and a black hole lies within, possessing 100 million solar masses.
-
Use of Coronavirus Pandemic Drones Raises Privacy Concerns: Drones Spread Fear, Local Officials Say

-
Coronavirus Hampers The Delivery Of Lockheed Martin F-35 Stealth Fighters For 2020

-
Instagram Speeds Up Plans to Add Account Memorialization Feature Due to COVID-19 Deaths

-
NASA: Perseverance Plans to Bring 'Mars Rock' to Earth in 2031

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
COVID-19: Doctors, Nurses Use Virtual Reality to Learn New Skills in Treating Coronavirus Patients