By Ana Verayo, | April 28, 2016
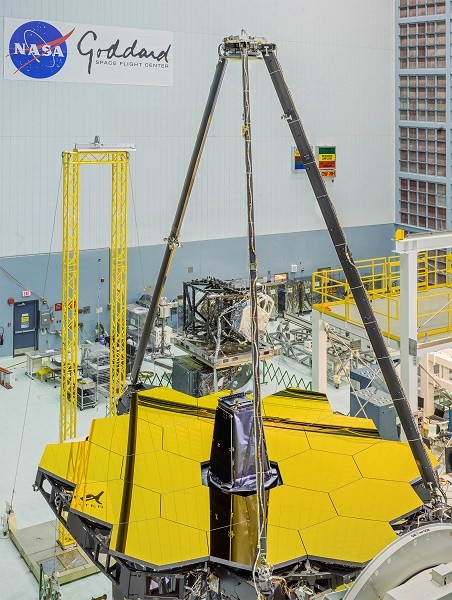

On April 27, 2016 engineers unveiled the giant golden mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope as part of the integration and testing of the infrared telescope at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland.
The Hubble Space Telescope's successor reveals more ultra high tech facilities, providing unprecedented views of more distant and unseen parts of the universe which could host life, not necessarily intelligent life but most probably microbial life forms.
Like Us on Facebook
With the new James Webb Space Telescope which is also the largest space telescope ever built, NASA engineers have revealed an eight meter gold coated mirror, which is also several times bigger than Hubble's. When it is fully deployed in space, it can span as long as a tennis court, becoming the world's leading space observatory in the next 10 years.
The US $10 billion telescope is nearing its completion at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland which will be launched in October 2018 aboard the Ariane 5 rocket from French Guiana in South America. The main mission of the Webb is to study the first light that shined in the universe after the Big Bang event and to search for star systems with habitable exoplanets.
The Webb will follow an orbit around the sun from a distance of 1.5 millio kilometers which will be ideal as it is far away enough to not become affected by Earth's light and heat. According to ICRAR-Curtin University astrophysicist Rob Soria, Webb is specifically designed to observe in infrared wavelengths so that most distant galaxies can be detected since they only appear in infrared. This would also mean that this can also provide more information about dark matter and dark energy which are the mysterious forces that continue to shape the universe.
Webb's bigger mirror also means that it can see much more farther and fainter objects than Hubble along with more color detection, to reveal the first galaxies that were formed in the cosmos. Scientists aim to study these very distant and faint galaxies to understand how the first batch of stars in the universe formed that alo formed the first galaxies.
With this new massive telescope, astronomers can now measure with more precision these earliest galaxies that are shaped together by unseen gravitational forces. Webb also carries special instruments unlike the Hubble, known as coronagraphs that can block light from nearby stars to easier detect the planets around those stars.
This means that these regions in nearby galaxies that are enshrouded in gas and dust can now be seen before newly formed stars blow them away with their solar winds. Finally, Webb can also reveal how planets are formed, shedding light on the earliest formation processes in our solar system.
-
Use of Coronavirus Pandemic Drones Raises Privacy Concerns: Drones Spread Fear, Local Officials Say

-
Coronavirus Hampers The Delivery Of Lockheed Martin F-35 Stealth Fighters For 2020

-
Instagram Speeds Up Plans to Add Account Memorialization Feature Due to COVID-19 Deaths

-
NASA: Perseverance Plans to Bring 'Mars Rock' to Earth in 2031

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
600 Dead And 3,000 In The Hospital as Iranians Believed Drinking High-Concentrations of Alcohol Can Cure The Coronavirus

-
COVID-19: Doctors, Nurses Use Virtual Reality to Learn New Skills in Treating Coronavirus Patients